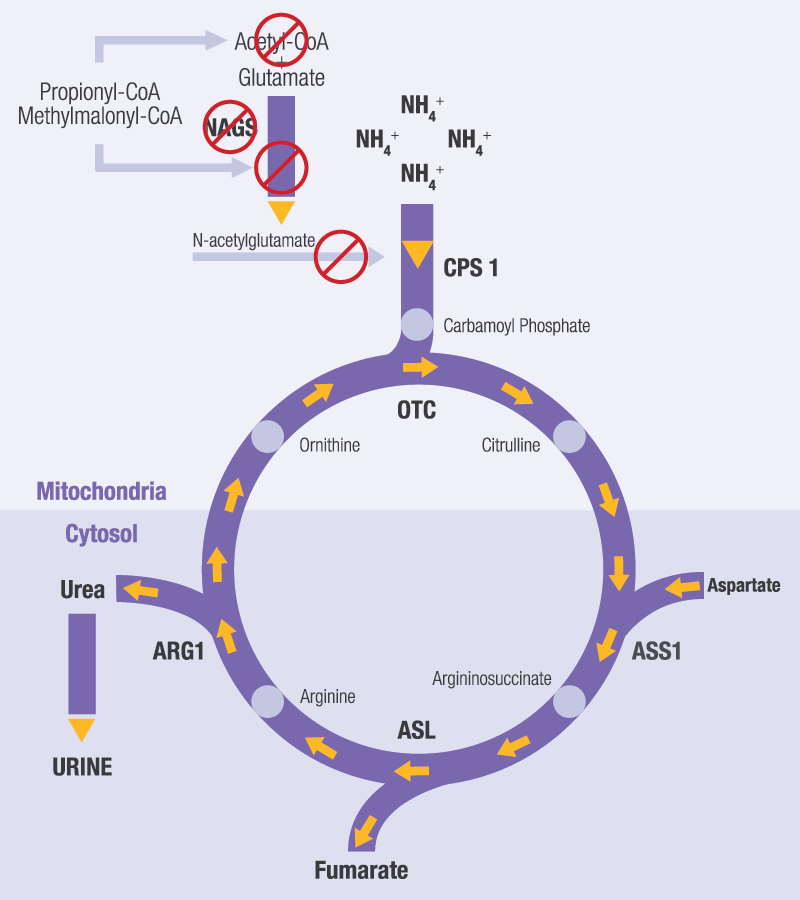
HOW CAN PROPIONIC ACIDEMIA AND METHYLMALONIC ACIDEMIA AFFECT THE UREA CYCLE?
If you have PA or MMA, your body lacks sufficient PCC or MUT enzyme activity to break down and use certain amino acids and fats. This causes toxins to build up in your body. Some of these toxins can block or impair your body’s urea cycle. The urea cycle processes and removes the excess ammonia in your body that is produced during the breakdown of protein.
To start the urea cycle, your body needs a compound called N-acetylglutamate (NAG). But the toxic substances that build up in PA and MMA may lead to less NAG production. Without sufficient NAG, the urea cycle will not work properly, resulting in the build-up of ammonia in your blood.